NorthEast RF, 531 Stuyvesant Ave, Union County, New Jersey 07083
Near Field Antenna Test Chamber
The StarLab antenna test range uses an array of 15 scanning probes spaced every 22.5° in an arch round the DUT (device under test). To perform a full sphere measurement the DUT is rotated 180° around the Z axis. The probes array can rotate over ± 11.25 in elevation, such that the probes are positioned in offset locations. This oversampling effectively fills in the gaps between the probes. Combined with the electronic scanning of the probes, the mechanical elevation scanning allows fast and fully automated measurements. This means that full 3D radiation pattern measurements can be performed very rapidly compared to conventional single-probe systems.
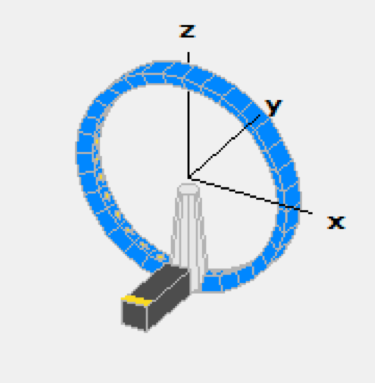
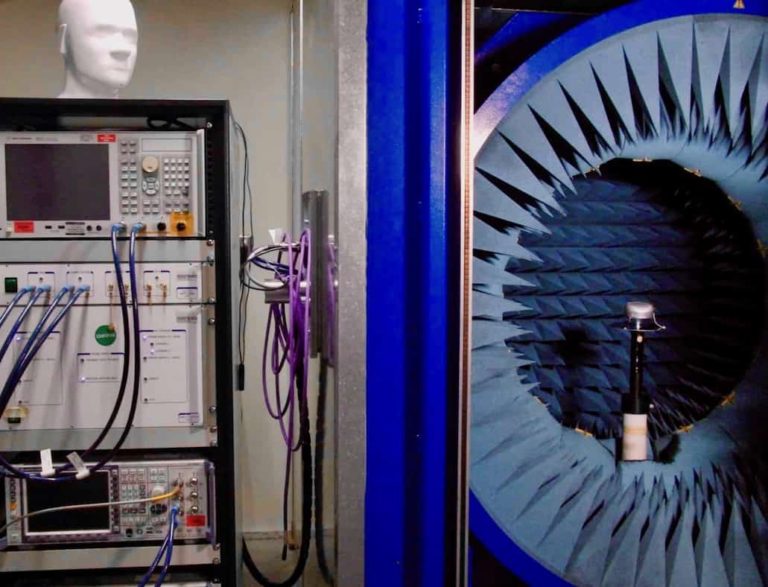
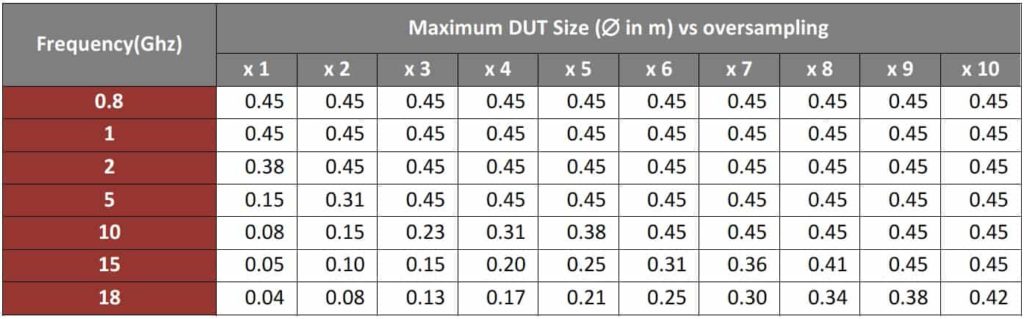
Oversampling - Resolution
The accuracy of the StarLab measurement system is a function of frequency, the diameter of the antenna, and the test system sampling resolution. For example, the table inset shows that oversampling the azimuth and elevation by a factor of x4 (22.5°/4 = 5.25°) results a maximum DUT size of 0.45 m at 5 GHz whilst maintaining the ± 1.1 dB peak gain accuracy. Note that with the correct calibration antennas the StarLab will work down to 0.65 GHz.
Peak Gain Accuracy
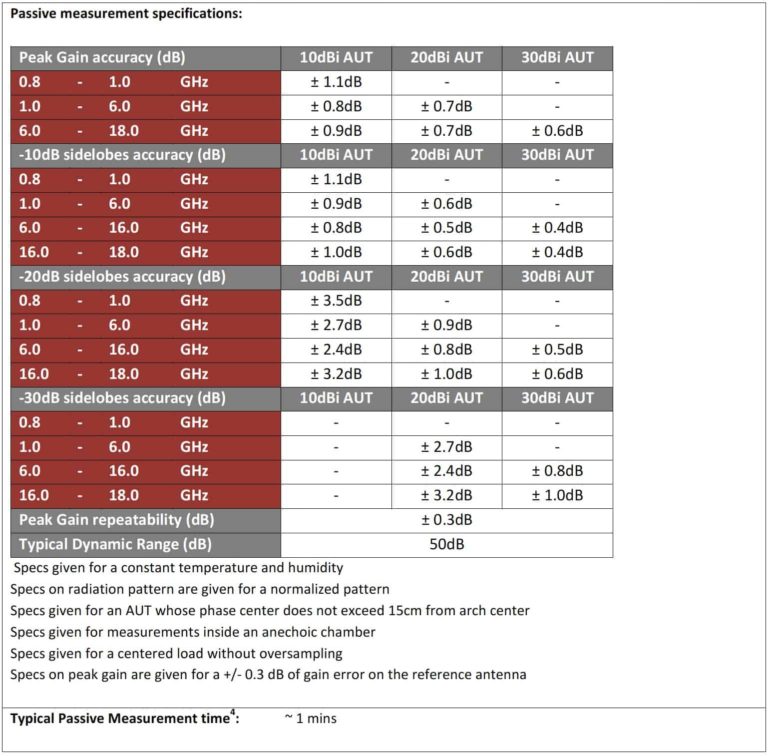
The full MVG near field anechoic test system performance specification can be found here.